Understanding Abandonment Trauma: Causes And Healing Approaches
Abandonment trauma can significantly impact an individual's emotional well-being, influencing relationships and self-perception in meaningful ways. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the definition and impact of abandonment, illuminating its various causes and forms. It emphasizes common signs to recognize and presents practical healing strategies, including therapeutic techniques and self-care practices. With a focus on the importance of seeking assistance, the discussion includes the benefits of therapy and guidance on how to identify a supportive therapist who meets specific needs. This article invites readers to engage in a journey toward understanding and healing from abandonment trauma.
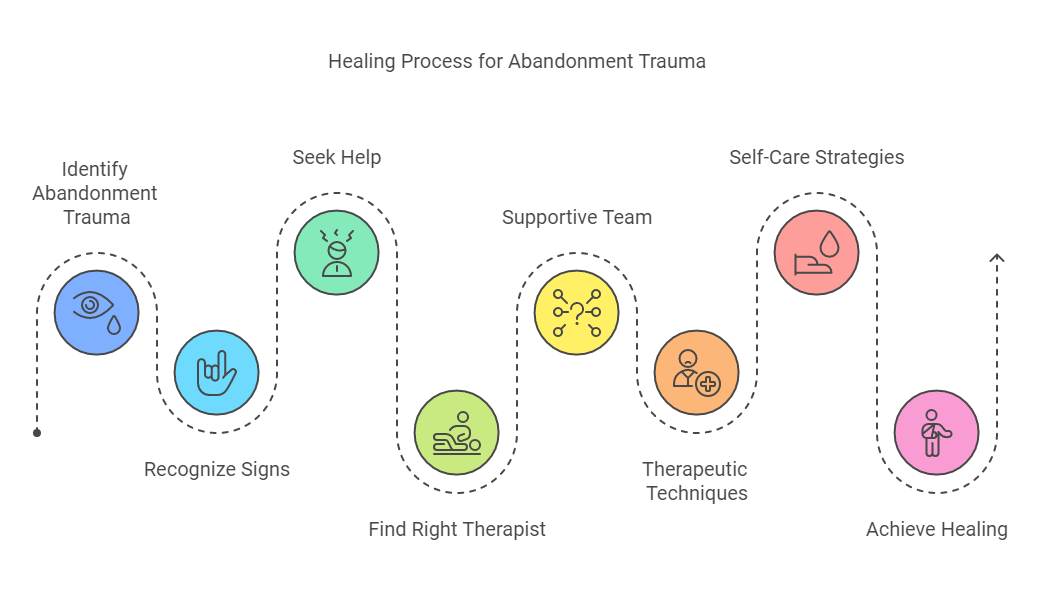
Key Takeaways:
Abandonment trauma can have a significant impact on a person's emotions and behaviors, and it is important to understand its causes and effects to effectively address it.
Recognizing the signs of abandonment trauma is crucial in seeking help and healing. Therapeutic techniques and self-care strategies can be effective in managing and overcoming its effects.
Seeking help for abandonment trauma is a brave and important step towards healing. Finding the right therapist and seeking support from a diverse and empathetic team can provide personalized care and promote confidentiality.
What is Abandonment Trauma?
Abandonment trauma pertains to the emotional and psychological consequences of experiencing feelings of abandonment, particularly during pivotal developmental stages such as childhood. This intricate issue frequently stems from various forms of loss, including childhood abandonment, emotional neglect, or family instability, and can result in considerable psychological distress in adulthood.
Individuals affected by abandonment trauma may encounter profound emotions, such as a pervasive fear of abandonment, which can manifest in maladaptive attachment styles and self-sabotaging behaviors within their interpersonal relationships.
Comprehending abandonment trauma is essential for facilitating effective healing and recovery, as it allows individuals to confront unresolved trauma and cultivate healthier connections with others.
Defining Abandonment and its Impact
Defining abandonment requires a comprehensive understanding of the various ways individuals may experience disconnection or lack of support, which can lead to enduring emotional scars and attachment issues.
This concept extends beyond mere physical absence to encompass emotional neglect, where caregivers may be present in a physical sense but fail to provide the necessary emotional support. Such experiences can have significant implications for attachment styles, influencing how individuals relate to others throughout their lives.
For example, individuals with secure attachment typically enjoy healthier relationships, whereas those exhibiting anxious or avoidant attachment styles may encounter difficulties with intimacy and trust, often stemming from past experiences of abandonment.
These attachment patterns not only affect relational dynamics but also have a considerable impact on psychological well-being. The emotional wounds resulting from these experiences necessitate awareness and healing to foster a healthier self-concept and improve interpersonal connections.
Causes of Abandonment Trauma
Abandonment trauma can arise from a variety of factors, such as childhood abandonment, family instability, and the emotional unavailability of caregivers.
These experiences can result in significant psychological effects.
Types of Abandonment and their Effects
There are several forms of abandonment that can result in trauma, including emotional neglect, which significantly impacts interpersonal relationships and contributes to overall psychological distress.
Emotional neglect, in particular, often leaves individuals feeling invisible and unworthy, as their emotional needs remain unacknowledged or unmet. This deficiency in emotional connection can manifest in various ways, including difficulties in forming close relationships and challenges in trusting others.
Physical abandonment, whether through actual separation or inconsistent presence, can evoke feelings of loneliness and insecurity. The resulting trauma may lead to difficulties in emotional regulation, resulting in heightened anxiety or impulsive behaviors.
Such experiences can hinder an individual's ability to establish healthy relationships, perpetuating a cycle of loneliness and distress that may persist into adulthood.
Recognizing the Signs of Abandonment Trauma
Recognizing the signs of abandonment trauma is essential for individuals to comprehend their emotional responses and behaviors, as these manifestations can present in various trauma symptoms and difficulties in forming connections.
Common Behaviors and Emotions
Common behaviors and emotions associated with abandonment trauma often include the need for reassurance, clingy tendencies, and increased sensitivity to rejection, all of which reflect significant emotional wounds.
These behaviors frequently manifest within various relationships, leading individuals to experience an overwhelming need for validation from partners, friends, or family members. This intense desire for acceptance can result in obsessive worries regarding potential abandonment, further complicating emotional stability.
Such heightened emotional responses can create a cycle of anxiety and fear, undermining trust and fostering insecurity. This struggle not only impacts personal feelings but also places considerable strain on interpersonal connections, highlighting the importance of recognizing these patterns and seeking healthy coping strategies.
By cultivating self-awareness and exploring therapeutic options, those affected by abandonment trauma can learn to effectively navigate their emotions and develop healthier relational dynamics.
Healing Approaches for Abandonment Trauma
Healing approaches for abandonment trauma include a variety of therapeutic techniques and self-care practices designed to facilitate trauma recovery and enhance overall psychological well-being.
Therapeutic Techniques and Self-Care Strategies
Therapeutic techniques, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), play a vital role in addressing abandonment trauma and promoting emotional regulation.
These methodologies equip individuals with practical tools to understand and reshape their thought patterns, facilitating healthier emotional responses to distressing memories and feelings. The incorporation of mindfulness strategies can enhance self-awareness and significantly alleviate anxiety.
It is important to emphasize that therapist support not only provides a safe environment for exploration but also customizes these approaches to meet the unique needs of each individual.
In trauma-informed care, professionals underscore the significance of trust and collaborative healing, ensuring that clients feel enableed throughout their journey, ultimately fostering resilience and supporting long-term recovery.
Seeking Help for Abandonment Trauma
Seeking assistance for abandonment trauma is a crucial step toward recovery, as various therapeutic modalities and support groups provide essential resources for enhancing psychological well-being.
Benefits of Therapy and Finding the Right Therapist
The benefits of therapy in addressing abandonment trauma encompass personalized care and effective therapeutic approaches that alleviate psychological distress. Such therapeutic strategies play a vital role in creating an environment where individuals can delve into their emotional pain without fear of judgment.
Identifying the appropriate therapist can significantly enhance the healing process, as a strong therapeutic alliance fosters a sense of emotional safety, enabling clients to confront challenging feelings and experiences with greater ease. Customized approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or attachment-based methods, enable individuals to rebuild trust in themselves and in others, ultimately facilitating the development of healthier relationships.
A therapist who is proficient in trauma-informed care possesses the skills necessary to guide clients toward resilience and self-acceptance, rendering recovery from abandonment trauma not only achievable but also profoundly transformative.
Confidentiality and Personalized Care
Confidentiality and personalized care are fundamental components of therapy for abandonment trauma, ensuring that clients feel secure throughout their healing journey.
These elements not only cultivate a trusting environment but also enable individuals to explore their vulnerabilities without the fear of judgment or breaches of privacy. When clients are assured that their personal experiences will remain confidential, they are more inclined to engage openly in the therapeutic process. This openness is essential for addressing deep-seated emotions and traumas.
Customized therapeutic approaches that take into account each individual’s unique history, preferences, and coping mechanisms further enhance emotional safety. Consequently, clients feel more valued and understood, thereby facilitating effective trauma recovery and fostering lasting change.
Supportive Team and Accessible Language
A supportive team and the utilization of accessible language are essential components in fostering an environment where individuals experiencing abandonment trauma feel understood and secure.
This nurturing atmosphere not only validates their emotions but also promotes open dialogue, enabling clients to articulate their fears and vulnerabilities without the risk of judgment.
When therapists and support staff communicate in a clear and empathetic manner, clients are better positioned to comprehend the therapeutic concepts being presented, thereby enhancing their engagement in the healing process. Such intentional communication acts as a bridge, minimizing the emotional distance often experienced in therapeutic settings and cultivating a sense of belonging.
Ultimately, by prioritizing emotional safety, individuals struggling with abandonment trauma can begin to rebuild trust and develop resilience on their path to recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is abandonment trauma?
Abandonment trauma refers to a psychological reaction to being separated or rejected by a significant person in one's life, such as a parent, partner, or caregiver. It can cause feelings of intense fear, shame, and worthlessness, and can have a significant impact on one's relationships and overall well-being.
What are the common causes of abandonment trauma?
Abandonment trauma can be caused by a variety of experiences, including neglect, physical or emotional abuse, sudden loss of a loved one, and abandonment by a significant person. It can also stem from childhood experiences, such as feeling emotionally disconnected from a parent or caregiver.
How does abandonment trauma impact relationships?
Abandonment trauma can lead to difficulties in forming and maintaining healthy relationships. It can cause individuals to fear intimacy, struggle with trust, and have low self-esteem. It can also result in patterns of self-sabotage and push people away, making it challenging to develop meaningful connections with others.
What are some common symptoms of abandonment trauma?
Individuals who have experienced abandonment trauma may exhibit symptoms such as anxiety, depression, feelings of emptiness, difficulty regulating emotions, and fear of being alone. They may also have a strong need for validation and seek excessive approval from others.
How can therapy help in healing abandonment trauma?
Therapy can be a valuable tool in healing abandonment trauma. A trained therapist can provide a safe and supportive space for individuals to explore their experiences and emotions. They can also help individuals develop healthy coping mechanisms, build self-esteem, and improve their relationships.
What are some effective healing approaches for abandonment trauma?
Some common healing approaches for abandonment trauma include cognitive-behavioral therapy, which focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, and attachment-based therapy, which addresses the root causes of attachment issues. Other approaches include somatic experiencing, art therapy, and mindfulness techniques. It is essential to find an approach that works best for each individual's unique needs.